What is Clinical Audit ?
and what it is not...
“Clinical audit is a quality improvement process that seeks to improve patient care and outcomes through systematic review of care against explicit criteria.”
Principles for Best Practice in Clinical Audit (2002, NICE/CHI

The key concepts of clinical audit are as follows:
- Clinical auditing is more than just data collection: it involves comparing current patient care and outcomes to explicit audit criteria (also known as standards).
- It is expected from the start that practice will be improved.
- Additional clinical auditing may be necessary to confirm that practice has improved.
THE EVOLUTION OF CLINICAL AUDIT
Clinical auditing by doctors was formalised for the first time in 1989. Prior to this auditing was a rare and isolated activity. Four years later, in 1993, Medical, Nursing, and Therapy audits were combined to form the multi-disciplinary activity known as clinical audit.
Since 2008, the national clinical audit strategy has shifted, resulting in the 'reinvigoration' of clinical audit at the local level. In line with this, the Department of Health has tasked the Health Quality Improvement Partnership (HQIP) and the National Clinical Audit Advisory Group (NCAAG) with overseeing national audits and leading the 'reinvigoration' of local clinical audit by promoting quality in healthcare and increasing the impact that clinical audit has on healthcare quality in England and Wales.
Clinical audit is linked to both clinical effectiveness and clinical governance.
First and foremost, clinical effectiveness “seeks to identify and evaluate existing evidence of best practice”. Once identified, local practice may be modified to ensure that it conforms to best practise.
Once implemented, a clinical audit project could be launched to ensure that:
- Best practises are followed.
- That the desired patient outcomes are obtained.
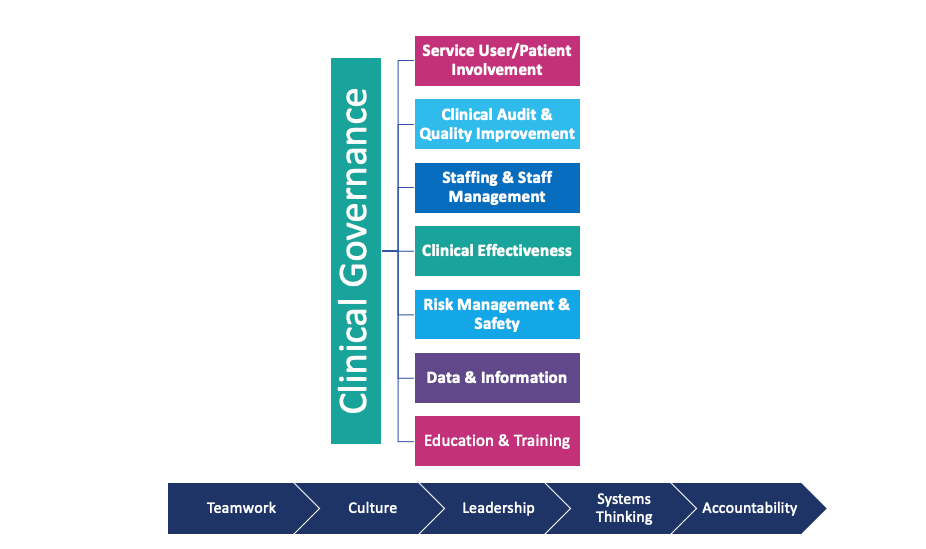
Second, care concerns are frequently identified through other clinical governance structures. Clinical audit comes under the Clinical Governance umbrella and forms part of the system for improving the standard of clinical practice.
Clinical governance is “a system through which healthcare organisations are accountable for continuously improving the quality of their services and safeguarding high standards of care by creating an environment in which excellence in clinical care will flourish."
The seven pillars of clinical governance include:
- Service User/Patient Involvement
- Clinical Audit & Quality Improvement
- Staffing & Staff Management
- Clinical Effectiveness
- Risk Management
- Data & Information
- Education & Training
These concerns are frequently then used to guide a clinical audit project. This includes the following:
· Patient feedback or complaints.
· Reporting of patient safety incidents/near misses
· Other priorities or concerns, like high volume, risk, or cost issues.
WHAT DOES A CLINICAL AUDIT ENTAIL ?
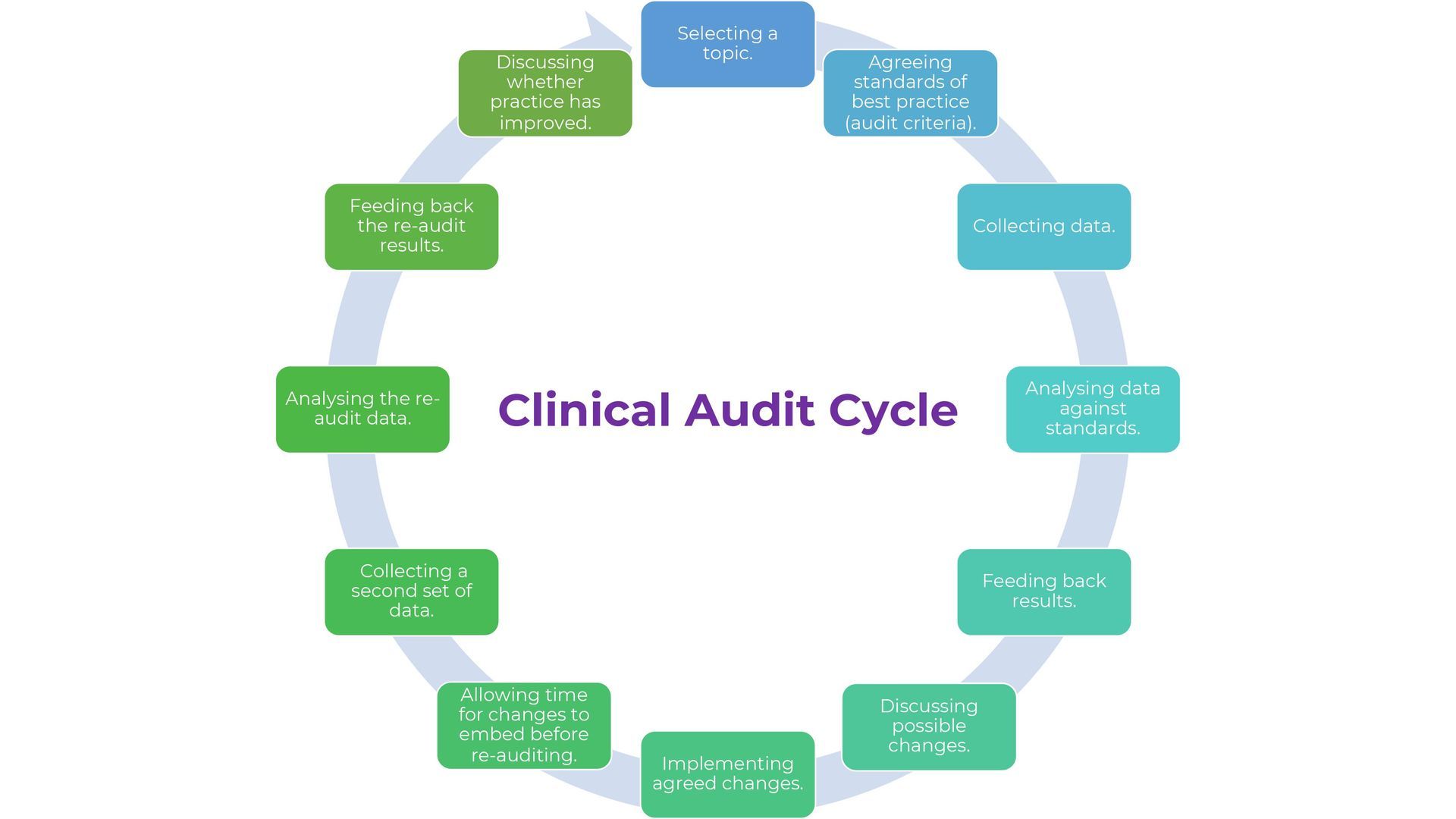
The main stages of the clinical audit process are:
- Selecting a topic.
- Agreeing standards of best practice (audit criteria).
- Collecting data.
- Analysing data against standards.
- Feeding back results.
- Discussing possible changes.
- Implementing agreed changes.
- Allowing time for changes to embed before re-auditing.
- Collecting a second set of data.
- Analysing the re-audit data.
- Feeding back the re-audit results.
- Discussing whether practice has improved.
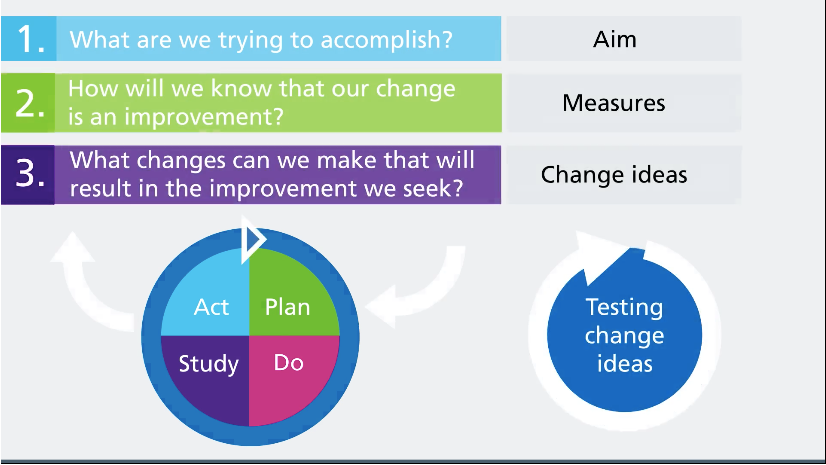
This process is called the : "Clinical Audit Cycle”.
WHAT A CLINICAL AUDIT IS NOT.
Clinical audit is not the only type of 'audit' that occurs in the care system. As part of a quality strategy, clinical auditing is a specific activity that measures clinical care against explicit audit criteria (standards). The term 'audit' can refer to a variety of things, and just because someone wants to 'audit' something doesn't mean they are doing or want to do a clinical audit project.
- Financial audit - Examining accounts to determine whether they provide a true and fair picture of the organisations financial position at a given time.
- Internal audit - An internal mechanism that tracks non-clinical activities and systems along 'audit paths' to determine whether things occurred as expected.
- Organisational audit - An external, independent, and voluntary audit of the whole organisation, based on a framework of explicit standards. Organisational audit looks at how well the organisation is set up and runs daily.
- Counting or checking things & Investigations - Clinical audit does not include the collection of data that is not related to explicit audit criteria (standards).
- Routine outcome/KPI monitoring - A clinical audit project may include the identification and measurement of clinical outcomes that are explicitly linked to the change process. Routine monitoring of outcome data for purposes such as performance monitoring, on the other hand, is not considered clinical audit.
- Surveys - Either of employees, patients, service users or carers .Surveys are typically conducted as part of engagement activity. They are primarily used to gather feedback from staff, patients, service users, or carers about treatment and/or care quality to determine if improvements can be made.
CLINICAL AUDIT vs CHECKLISTS: WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE?
Clinical audits and checklists are both useful tools in healthcare for improving quality and patient safety. These two methods, however, have significant differences but are very often confused.
The checklist is one of the most basic and widely used quality planning and control tools. A checklist, at its most basic, is simply a list of items to be completed to complete a task and demonstrate that these were completed as planned.
A checklist should not be confused with a "Clinical Audit," which is a quality assurance tool that provides a systematic review of the quality of care provided, highlighting areas for improvement and best practises. It entails reviewing patient records and clinical processes for discrepancies and determining whether the care provided is in line with recommended clinical evidence, audit will also have some level of standard to be achieved.
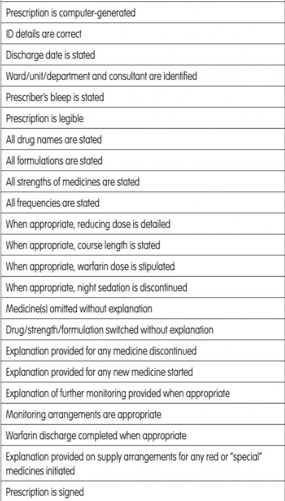
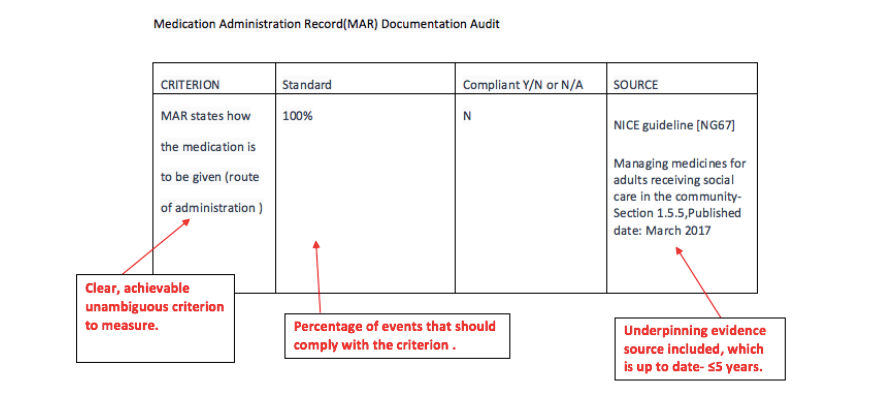
While both clinical audit and checklists are important quality tools , clinical audit is a more comprehensive and thorough approach to evaluating care quality, whereas checklists are a specific tool used to ensure that steps in procedures are followed.Look at the examples below of both a checklist and an audit criteria example. What differences can you see ?
Example Medication Checklist below:
EXAMPLE MEDICATION CLINICAL AUDIT CRITERIA BELOW:
Email Us
For general enquiries & questions,
contact us via email
Book Free Consultation
Need some advice face to face? Book a free 30 minute MS Teams consultation
CHECK OUT OUR OTHER BLOG POSTS
Knowledge Hub





Merlin House I Langstone Business Park
Newport I NP18 2HJ
Copyright © 2024 Advanced Clinical Solutions Ltd . All rights reserved
Company Reg : 10293607 VAT Reg: 290 6883 65